Urban landscapes are more than just city streets and buildings—they are vibrant ecosystems that contribute to the quality of life for city dwellers. Green spaces, including trees, play a crucial role in enhancing the aesthetic appeal, improving air quality, and providing shade. In the realm of urban tree management, tree pollarding has emerged as a vital technique for maintaining the health and appearance of trees in confined spaces. This blog explores how tree pollarding can revitalize urban landscapes and its significant role in city planning.
What is Tree Pollarding?
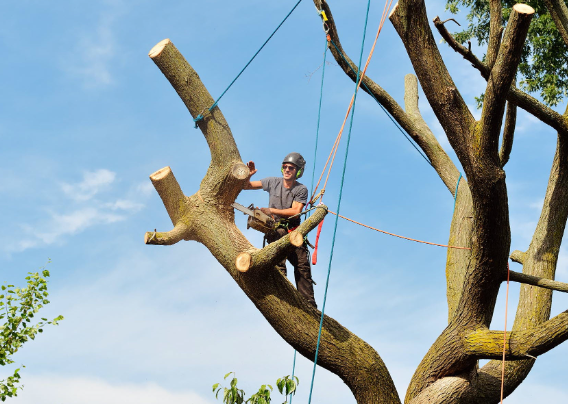
Tree pollarding is a specialized tree maintenance technique designed to control the size and shape of trees. Unlike standard pruning, which removes branches to promote healthy growth, pollarding involves cutting back all limbs to the main trunk. This process encourages the growth of lateral branches, which helps manage the tree’s size and shape while prolonging its lifespan.
Historically, pollarding was used for practical purposes, such as providing materials for thatching or fodder for livestock. Today, it is primarily employed in urban environments to manage tree size and maintain safety.
The Technique of Tree Pollarding
The tree pollarding process involves several key steps:
Initial Cutting: All limbs are cut back to the main trunk, typically at a height of two or three meters above ground level. This drastic reduction in foliage is essential for controlling the tree’s size.
Encouraging Regrowth: After the initial cut, the tree is allowed to regrow. This regrowth will primarily consist of lateral branches, which are more manageable and less likely to interfere with structures or overhead utilities.
Pollarding not only keeps trees at a manageable size but also ensures that they do not become a hazard due to falling dead wood.
Benefits of Tree Pollarding in Urban Landscapes
Control Over Tree Size: In urban areas, space is often limited. Pollarding helps manage tree size, ensuring that trees do not outgrow their allotted space or interfere with buildings, streets, or utility lines. For example, pollarding is beneficial in areas with restricted soil space or where trees are planted close to structures.
Enhanced Safety: Tree safety is a significant concern in urban areas. By removing dead or potentially hazardous branches, pollarding reduces the risk of falling debris. This is particularly important in high-traffic areas or near pedestrian pathways. Cities that have implemented pollarding have seen a decrease in tree-related accidents and maintenance issues.
Aesthetic and Environmental Benefits: Pollarded trees contribute to urban aesthetics by maintaining a neat and uniform appearance. Additionally, pollarding helps preserve the health of trees by preventing overcrowding of branches and allowing better air circulation. This technique supports the overall health of urban green spaces, contributing to a more pleasant environment.
Pollarding and Urban Planning
Integrating tree pollarding into urban planning involves several best practices:
Assessment and Planning: Urban planners should assess the specific needs of each tree, considering factors such as species, location, and growth patterns.
Regular Maintenance: Scheduled pollarding ensures that trees remain healthy and properly managed over time.
Community Involvement: Engaging the community in tree care practices can enhance public support and awareness of the benefits of pollarding.
Successful urban planning projects often include pollarding as part of their green space management strategies. Cities like London and Paris have long histories of using this technique to maintain their historic urban trees.
Takeaway
Tree pollarding is a valuable tool in urban tree management, helping to control tree size, enhance safety, and contribute to the aesthetic appeal of city landscapes. By incorporating pollarding into urban planning strategies, cities can revitalize their green spaces and ensure that trees continue to thrive in an urban environment. Urban planners, developers, and local governments are encouraged to consider tree pollarding as a key element in their landscape management practices.